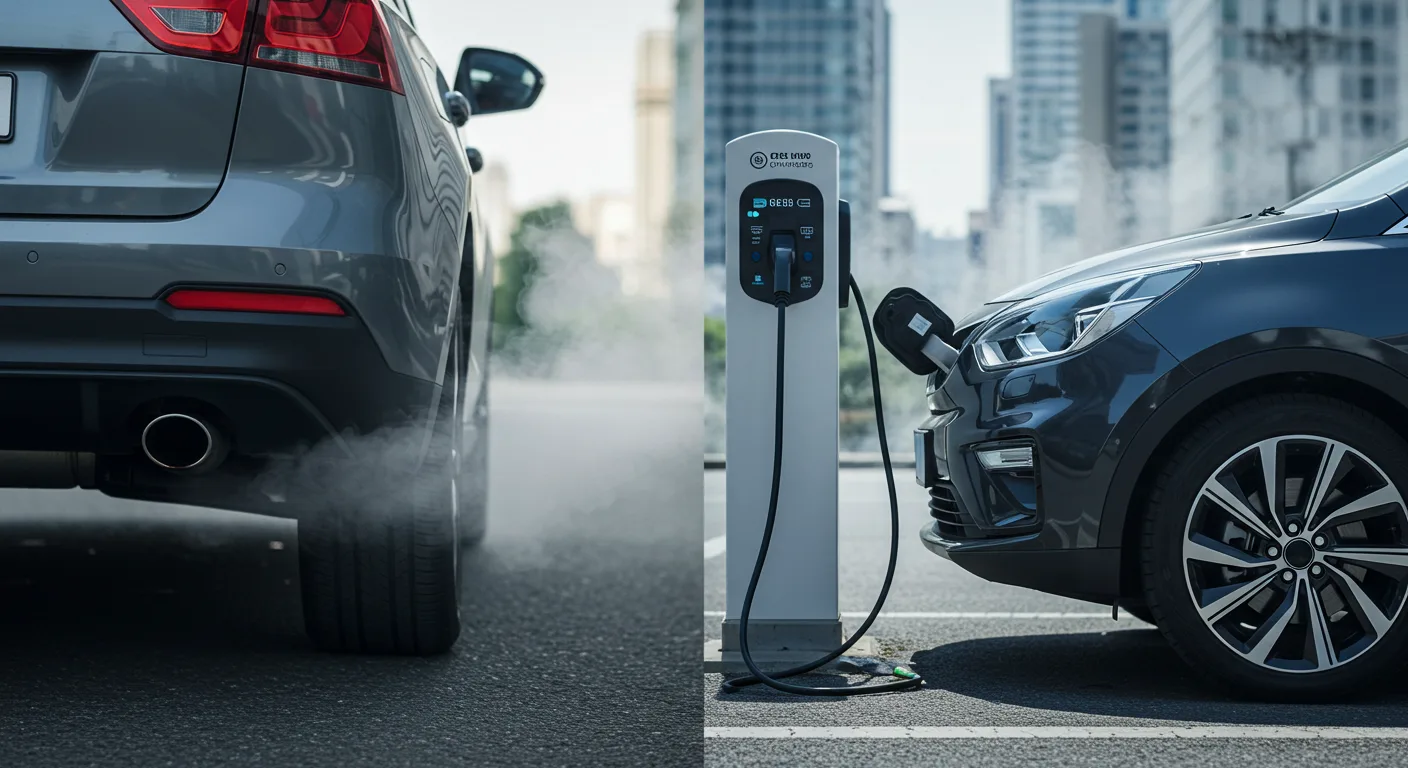
Do Electric Cars Need Catalytic Converters?

Electric vehicles (EVs) have transformed the automotive landscape, offering a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. A common question that arises is, “Do electric cars have catalytic converters?” Since EVs produce no exhaust emissions, they do not require catalytic converters, which are essential in gasoline vehicles for reducing harmful pollutants. To answer this, it’s essential to understand the role of catalytic converters, the emission profiles of electric cars, and the fundamental differences between EVs and gasoline vehicles.
Why Do Gasoline Cars Have Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are critical components in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, serving to reduce the emission of harmful pollutants from an engine’s exhaust gases. They work by converting toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. This process significantly improves air quality and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
Key functions of catalytic converters include:
- Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Breaking down NOx into nitrogen and oxygen, thereby reducing smog formation.
- Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide (CO): Converting CO into carbon dioxide (CO₂), a less harmful gas.
- Oxidation of Unburned Hydrocarbons (HC): Transforming hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water, reducing toxic emissions.
The implementation of catalytic converters has been instrumental in reducing vehicle emissions since their widespread adoption in the 1970s.
Do Electric Vehicles Produce Emissions?
Electric vehicles are often lauded for their environmental benefits, primarily due to their emission profiles.
Tailpipe Emissions:
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions: EVs produce no exhaust emissions, as they do not combust fuel. This absence of tailpipe pollutants contributes to improved air quality, especially in urban areas.
Lifecycle Emissions:
- Electricity Production: While EVs themselves do not emit pollutants during operation, the generation of electricity used to charge them can produce emissions, depending on the energy sources.
- Manufacturing Impact: The production of EV batteries involves energy-intensive processes, which can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. However, studies indicate that EVs typically result in lower overall emissions compared to gasoline cars, even when accounting for manufacturing and electricity generation.
Key Points:
- No Combustion: EVs operate without burning fossil fuels, eliminating traditional exhaust emissions.
- Energy Source Matters: The environmental impact of charging EVs depends on the cleanliness of the electricity grid, with renewable energy sources offering the most significant benefits.
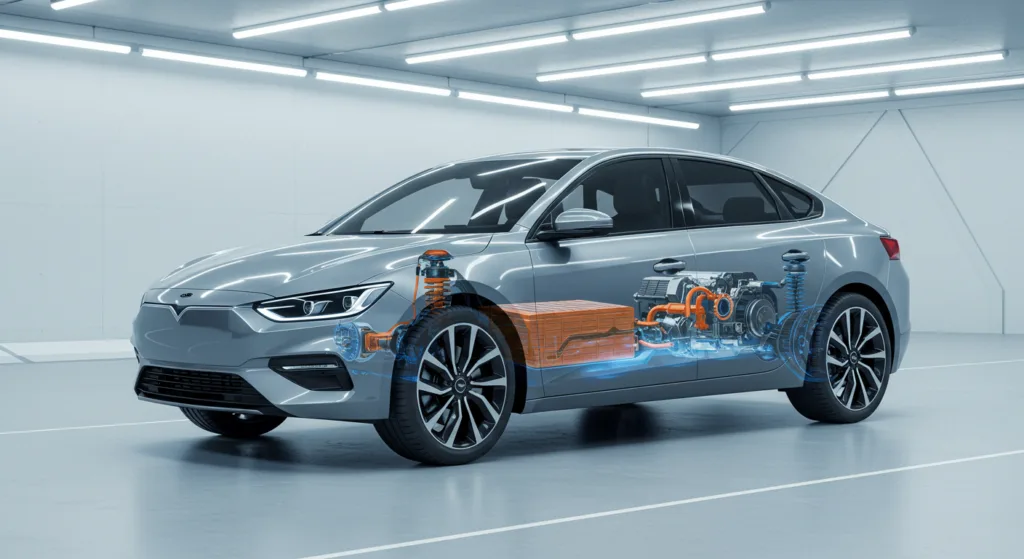
What Makes EVs Different from Gas Cars?
Understanding the distinctions between electric vehicles and gasoline-powered cars clarifies why certain components, like catalytic converters, are unnecessary in EVs.
Propulsion Systems:
- Gasoline Cars: Utilize internal combustion engines that burn fuel, producing power along with various emissions.
- Electric Vehicles: Rely on electric motors powered by energy stored in batteries, resulting in a clean and efficient propulsion method.
Emissions:
- Gasoline Cars: Emit pollutants such as CO₂, NOx, CO, and unburned hydrocarbons, necessitating emission control devices like catalytic converters.
- Electric Vehicles: Lack tailpipes and do not produce exhaust emissions during operation.
Maintenance and Components:
- Gasoline Cars: Require regular maintenance of components like catalytic converters, exhaust systems, and oil changes.
- Electric Vehicles: Have fewer moving parts, leading to reduced maintenance needs and the absence of components related to fuel combustion.
Environmental Impact:
- Gasoline Cars: Contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, impacting climate change.
- Electric Vehicles: Offer a pathway to lower emissions, particularly when charged with renewable energy sources, supporting global decarbonization efforts.
In summary, the inherent design and operation of electric vehicles eliminate the need for catalytic converters, as they do not produce the harmful emissions associated with fuel combustion. This fundamental difference underscores the environmental advantages of transitioning to electric mobility.
Know the Difference – Unlike gas cars, electric vehicles don’t burn fuel, so they don’t need a catalytic converter to filter emissions.
How Do Catalytic Converters Work in Traditional Cars?
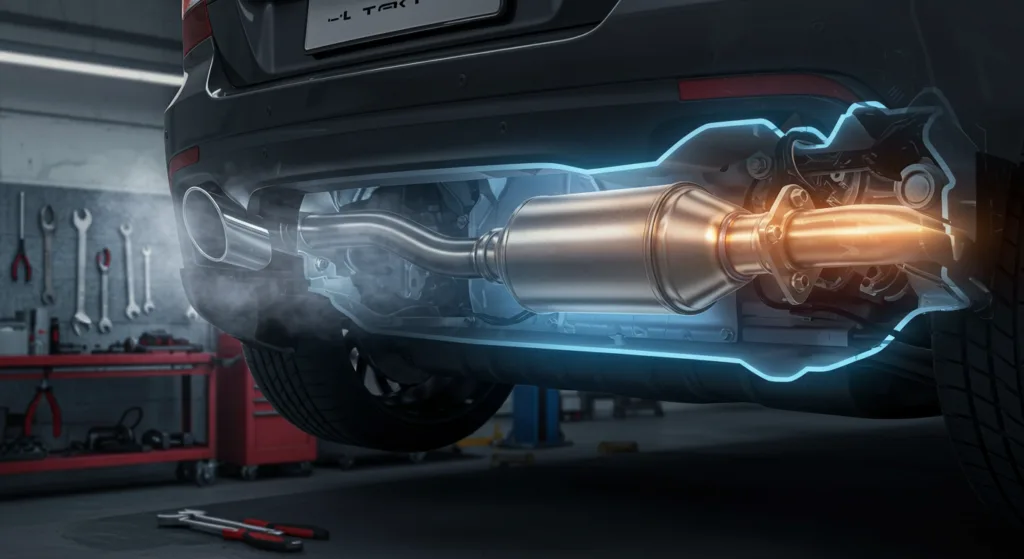
Catalytic converters are essential components in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, designed to reduce harmful emissions produced during fuel combustion. Understanding their function and necessity highlights why electric vehicles (EVs) do not require these devices.
What Is the Purpose of a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter serves as an exhaust emission control device that transforms toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. This process is vital for reducing the environmental impact of gasoline and diesel vehicles.
Key Functions:
- Reduction of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Breaking down NOx into nitrogen and oxygen, thereby reducing smog formation.
- Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide (CO): Converting CO into carbon dioxide (CO₂), a less harmful gas.
- Oxidation of Unburned Hydrocarbons (HC): Transforming hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water, reducing toxic emissions.
By performing these functions, catalytic converters significantly decrease the release of harmful substances into the atmosphere, contributing to improved air quality and public health.
How Do Catalytic Converters Reduce Emissions?
Catalytic converters utilize a catalyst, typically composed of precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium, to facilitate chemical reactions that convert harmful emissions into less harmful substances. The internal structure often consists of a ceramic honeycomb coated with these catalysts, providing a large surface area for reactions to occur efficiently.
Process Overview:
- Exhaust Gas Enters: Hot exhaust gases containing pollutants such as NOx, CO, and HC enter the catalytic converter.
- Catalytic Reaction: As these gases pass through the catalyst-coated honeycomb, chemical reactions occur:
- Reduction Reaction: NOx is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen.
- Oxidation Reaction: CO is oxidized to CO₂, and HC is oxidized to CO₂ and water.
- Cleaner Emissions Exit: The converted, less harmful gases are then expelled through the vehicle’s exhaust system.
This process effectively reduces the emission of pollutants, ensuring vehicles comply with environmental regulations and contribute less to air pollution.
Why Don’t Electric Cars Use Catalytic Converters?
Electric vehicles (EVs) operate fundamentally differently from internal combustion engine vehicles, leading to the absence of catalytic converters in their design.
Key Differences:
- No Fuel Combustion: EVs are powered by electric motors and batteries, eliminating the need for burning fossil fuels. Consequently, they do not produce exhaust gases that contain pollutants like NOx, CO, or HC.
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions: Since there is no combustion process, EVs do not have tailpipes or exhaust systems, and therefore, no emissions that would require treatment by a catalytic converter.
As a result, the primary function of catalytic converters—to reduce harmful emissions from combustion—is unnecessary in electric vehicles. This design difference contributes to the environmental benefits of EVs, aligning with global efforts to reduce air pollution and combat climate change.
Understanding the role of catalytic converters in traditional vehicles and their absence in electric cars underscores the environmental advantages of transitioning to electric mobility. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the adoption of EVs plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and promoting sustainability.
🔋 “Electric cars don’t just change the way we drive—they change the air we breathe.”
What Parts Replace a Catalytic Converter in EVs?
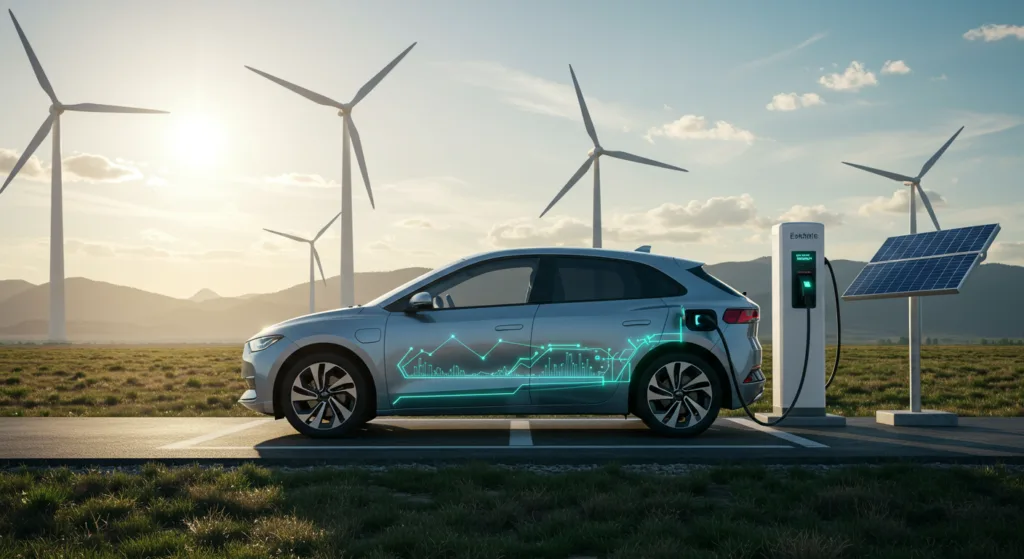

Electric vehicles (EVs) operate without internal combustion engines, eliminating the need for catalytic converters. Instead, they rely on specific components that contribute to their efficient and eco-friendly performance.
Do Electric Cars Have Emission Control Systems?
Traditional vehicles utilize emission control systems, including catalytic converters, to reduce harmful pollutants produced during fuel combustion. In contrast, EVs do not produce tailpipe emissions, as they operate without combustion processes. Therefore, they do not require conventional emission control systems.
Key Points:
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions: EVs produce no exhaust emissions, eliminating the need for components like catalytic converters.
- Alternative Emission Considerations: While EVs do not emit pollutants during operation, emissions may occur during electricity production used for charging, depending on the energy source.
What Are the Key Components of an Electric Vehicle?
EVs comprise several essential components that replace traditional engine parts, ensuring efficient and clean operation.
Primary Components:
- Battery Pack: Stores electrical energy to power the vehicle.
- Electric Motor: Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the wheels.
- Power Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for the motor.
- Charging System: Allows the vehicle to connect to external power sources for recharging.
- Thermal Management System: Regulates temperatures of the battery and motor to maintain optimal performance.
These components work together to provide a seamless and efficient driving experience without the need for traditional emission control devices.
How Do EVs Stay Environmentally Friendly Without One?
EVs maintain environmental friendliness through their inherent design and operational efficiencies.
Contributing Factors:
- No Combustion Process: Eliminates tailpipe emissions entirely.
- Efficient Energy Use: Electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines, reducing overall energy consumption.
- Renewable Energy Compatibility: Charging EVs with renewable energy sources further minimizes their environmental impact.
By leveraging these factors, EVs offer a sustainable alternative to traditional vehicles, contributing to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
✅ No exhaust system means no emissions – Unlike gas cars, EVs don’t release CO₂, NOx, or other harmful pollutants.
Do electric cars have catalytic converters? No, because EVs don’t produce exhaust emissions, eliminating the need for one. Instead, they rely on clean energy and efficient components like electric motors and battery packs. As the world moves toward greener transportation, EVs play a key role in reducing pollution.
If you found this article helpful, share it on social media to spread awareness about the future of electric mobility! 🚗⚡



